'Examining Stakeholders' Views & Opinions for River Conservation in India
– a case study from Pune, Maharashtra
By: Nishikant Gupta | Date: 21st September 2019
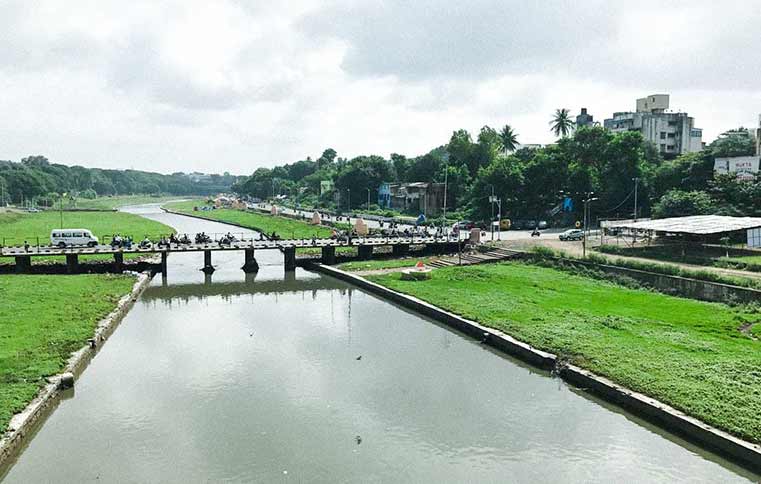 Image Source: Mandar Badve- Medium
Image Source: Mandar Badve- Medium
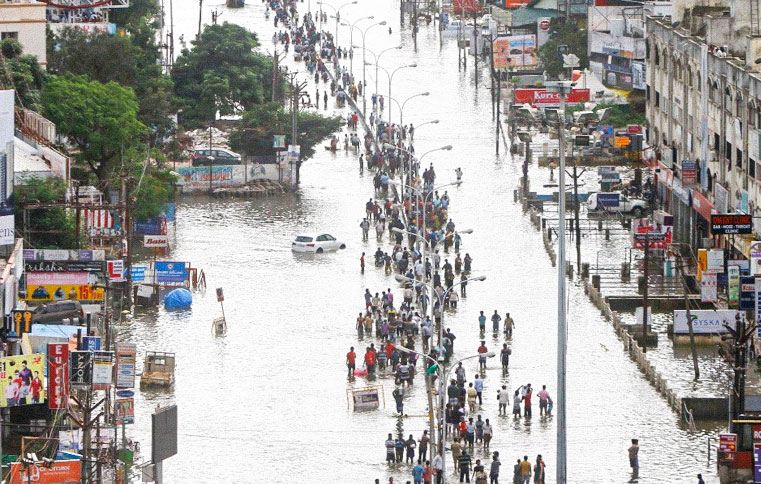
An online survey conducted between 2016 and 2017 to assess the views and opinions of the residents of Pune city regarding their rivers resulted in 160 responses, where 98% of the respondents mentioned that the rivers need protection.
A March 2018 paper published in the journal NeBIO – An international journal of environment and biodiversity entitled, “Examining stakeholders’ views and opinions for river conservation in India: a case study from Pune, Maharashtra” stresses that “there is a requirement to promote sustainable use of available water, and it is essential to inform the local communities of water storage techniques in view of the current status of water availability in the city”.
The research conducted and co-authored by Dr. Nishikant Gupta and Mr. Ishaan Kochhar is built on a web-based survey which was conducted between 2016 and 2017 to understand the views and opinions of the residents of Pune city regarding their rivers and its conservation needs.
The authors point out that “based on the current findings, there is an urgent need for actions to assist the rivers and dependent communities”. The authors conclude their paper by providing a series of recommendations at various levels of governance:
(a) Strengthen field and spatial-temporal data by conducting periodic assessments of changes in overall river ecology – capacity building of identified research agencies/ institutions can assist with this data collection;
at the local stakeholder level, education and awareness training will be key towards supporting cleanliness drives and reducing pollution;
(c) water resources management policies/legislations should be harmonized in the local context;
(d) there is a need to strengthen the existing institutional capacities to regularly assess and forecast the water demand, allowing the development of technical guidance/support tools; and
(e) there is a requirement to promote sustainable use of available water, and it is essential to inform the local communities of water storage techniques in view of the current status of water availability in the city.
Key Research Points
1. Rivers are threatened by numerous stressors, and the projected impacts of climate change warrants strategies for their protection.
2. The rivers of the district of Pune in Maharashtra, India face severe threats despite being a lifeline for some local communities.
3. Pollution (47%) and management issues (25%) were identified as the dominant adverse issues, and legislative support (31%) a potential protective measure. Overall, 73% of the respondents felt that protecting their rivers could possibly assist with water shortages (in varying degrees).
4. An examination of Global Surface Water Explorer datasets (1984-2015) revealed that over a span of 32 years, new surface waterbodies had appeared, and significant ones had disappeared from the city.
5. Incorporating stakeholders’ views and opinions in conservation policies can assist with their sustainability and success.