Water Purification Strategies - Tahaan
By: Ishwari Latey | Date: 10th January 2019

Since ancient time, human lives have revolved around a river. The river has caused many civilizations, the very name “India”, was given by the west to this ancient land was associated with the river, the land which resides in the valley of river Indus. The foundation of agriculture, the mere fact of the human conversion from ancient hunter-gatherer to a farmer and all the aftermath which followed which is the prominent reason why human civilization is as it is today; the statement “It is all because of a river” does not seem far fetched.
It seems that humans have neglected the very reason for his existence very conveniently. To revive a river is no easy task. In fact, it is the most difficult task to master. The most important is to define what ‘restoration’ means.
Will we ever able to make the river before we deemed it fit to dump our unwanted burden into her? We cannot imagine the damage which we have caused. The most adverse thing is, we don’t know how to manage the unwanted burden we created! Our ancestors did invent things without the concern of fallout strategies..
Strategies for water purification : (Mohiyaden, Sidek et.al 2016)
In Malaysia, River water purification is considered as a new approach and the implementation is still on a fundamental basis. Currently, water quality improvement efforts are focused primarily on point source measures such as sewerage treatment, pertinent regulation, and wastewater treatment. Japan and Korea have implemented this treatment technology about a decade ago.
Shows the concept of river purification measures which are being implemented in Japan, China, and Korea.
The following figure shows the concept of river purification measures which are being implemented in Japan, China, and Korea. We will be reviewing the concept of “Direct Purification” in this article.
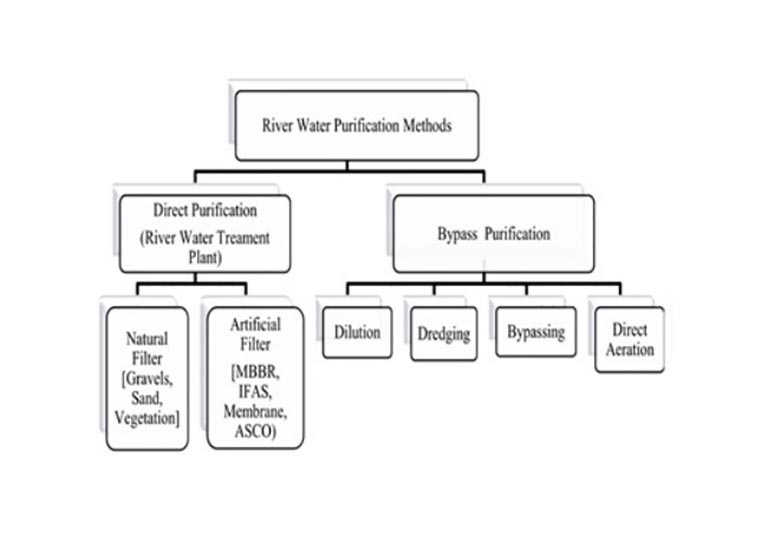
Polluted river water is conveyed to a water purification facility which then returns the decontaminated water to the river and directly reduces pollutants at the facilities. Polluted river water is conveyed to a water purification facility which then returns the decontaminated water to the river and directly reduces pollutants at the facilities.
This experiment in China used the soil as media to simulate the purification capability of the river water under natural conditions. F. Zhang et al. (2010) analyzed a series of soil samples and water sample tests, and the regularity of filtering purification capability patterns towards types of media to polluted water. Natural filters like sand, grovels and vegetation is an effective way of natural purification.
Artificial filtration is also mostly applied in river purification projects. An artificial biological filter is originally adapted from wastewater treatment plant technology. The evidence of artificial filter can be clearly seen in the application of MBBR, and IFAS systems.
In broad water industry term, MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) is an upgraded activated sludge with a suspended biological carrier in a complete mix and continuous flow which combine attached growth process and suspended growth process.
On the other hand, IFAS (Integrated Fixed Film Activated Sludge) is a hybrid suspended growth - a bio-film system that incorporates a high surface area of fixed or free floating media in the oxygen-deprived or enriched zones of the conventional activated sludge process (CAS).
The difference between IFAS and MBBR is that in the IFAS system, the activated sludge from the sludge re-circulation is additionally used, which means that the combination of activated sludge and carrier-fixed bio-films is used in the same reaction tank volume. We will see these innovations in detail in the future.
In simple terms, In MBBR the activated sludge (aerated sewage containing aerobic microorganisms which help to break it down.) is moving and in IFAS it is fixed in a particular area to deposit the contaminants.
Bypass purification :
In the river, the dilution process is able to improve polluted water quality. It introduces an entry of clean water from a tributary into a polluted main river thus increasing the flow volume of main river proportion to the introduced water quantity.
In a tidal river (A river whose flow and level are influenced by tides such as the Brahmaputra, Ganga rivers) this method improves water quality by the alternating tidal current regime due to reverse flow of the tidal river and the increment of Dissolved oxygen in the water. This method involves moderate expenses for constructing diversion and conveyance facilities including operation cost.
In the future, we will see many interesting methods like these which can be used for water purification in Indian rivers. If we want our future generations not to know the river just by its pictures, we ought to do something. It might take years, but it is our duty towards our very origin. She deserves to be able to flourish other souls, just like we did, by her.